

Calf pain
1,Shin splint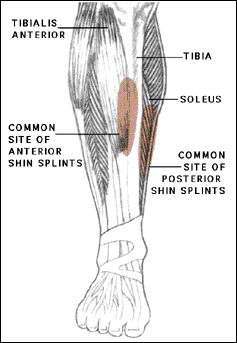
Shin splint is an umbrella concept, which still mostly remains unclear. The common accepted explanation is medial tibial traction periostitis, which means calf muscles pulling on connective tissue covering the shin bone.
Signs and symptoms:
- Diffuse pain along the medial (lateral) border of the shin bone,
- The pain can affect patient’s activity, but usually patient can finish it,
- But more pain after the activity and following morning.
Treatments:
- In the acute stage, symptomatic relief is the priority, such as cold/heat, NSAID.
- Normally, physiotherapist will provide deep tissue massage, proper stretch, acupuncture, and taping for patient, also remember to wear proper shoes.
2, Calf muscle injury
This is very common site for muscle injury, normal Gastrocnemius and Soleus.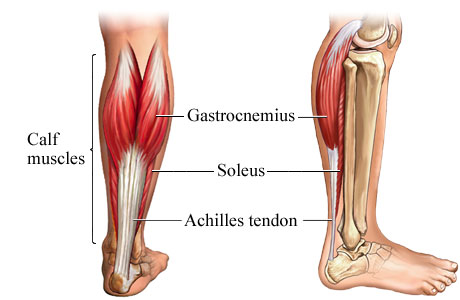
Signs and symptoms:
- Acute calf pain after injury
- Local tenderness
- Pain with ankle stretch and standing on toes
Treatments:
- Acute phase, same as other muscle injuries, RICE, STM, AROM exercise, acupuncture, stretch
- Rehabilitation phase, balance retraining is important for lower limb injury, endurance exercise, agility exercise and power training are also important.
3, chronic compartment syndrome:
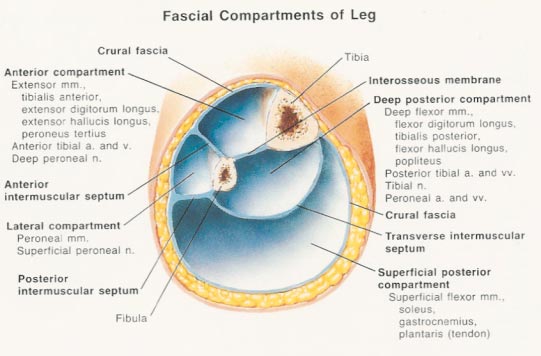 There are four compartments in leg region, most common compartment syndromes happen in posterior compartment, which means pain in the calf. Chronic compartment syndrome is the pressure in the deep comparment incresasing with activities which compresses blood supply.
There are four compartments in leg region, most common compartment syndromes happen in posterior compartment, which means pain in the calf. Chronic compartment syndrome is the pressure in the deep comparment incresasing with activities which compresses blood supply.
Signs and symptoms:
- Ache with running, more pain with prolonged running, sometimes patient has to stop running.
- PNN in calf or sole of foot
- Local tightness
Treatments:
- Acute phase: resting, hot/cold, stretch, acupuncture
- Rehabilitation phase: regular stretch and STM